Why Gabon?
Offshore Gabon offers significant material prospectivity in new and proven oil plays along the margin. The offshore area may be divided by geology into three distinct areas; North, Central, and South.
Although exploration has been undertaken in shallow waters along this whole margin, exploration for oil trapped in reservoirs that have never been seen before, on state-of-the-art seismic data with well data to understand the working of the hydrocarbon system, gives new investment opportunities to discover significant volumes of new oil.
Data Library
Search our interactive map portal to see the industry-leading subsurface data we offer in Gabon. View available data types, projects and deliverables in your areas of interest.
Our Data
TGS has acquired 16,900 km2 of long offset 3D seismic in the Gabonese shallow water, and over 10,000 km2 of 3D seismic reprocessing in deeper water.TGS has reprocessed an initial volume of 10,879 km2 through a broadband (de-ghosted) PreSTM sequence and Kirchhoff PreSDM. These data were originally acquired in 2014 on a proprietary basis and for this reason, have been unavailable publicly until recently. Final PreSTM products are available now.
TGS holds over 20,000 km of 2D seismic data offshore Gabon in addition to Marine Gravity and Magnetic surveys. This data gives a regional overview and highlights key areas of exploration.
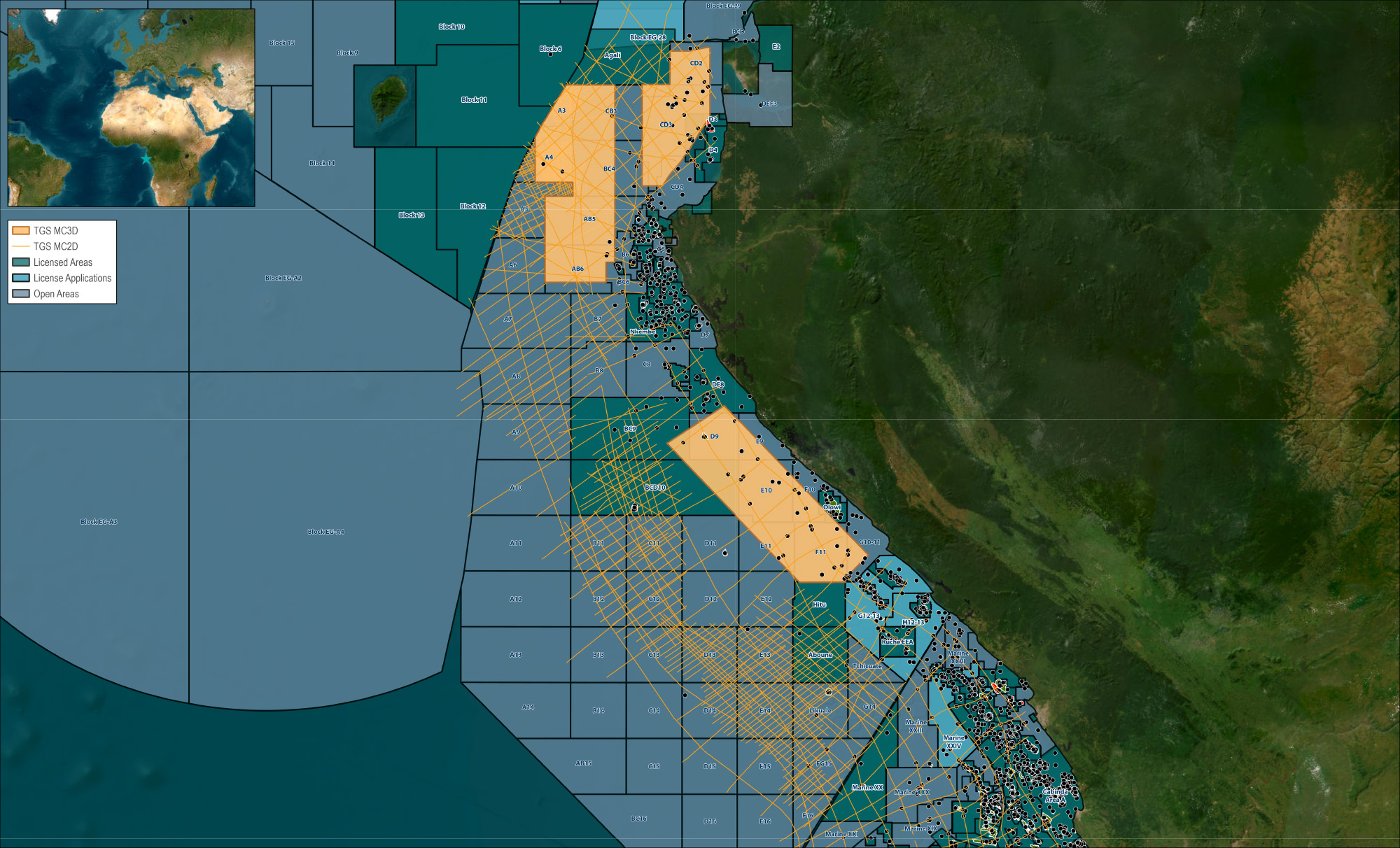
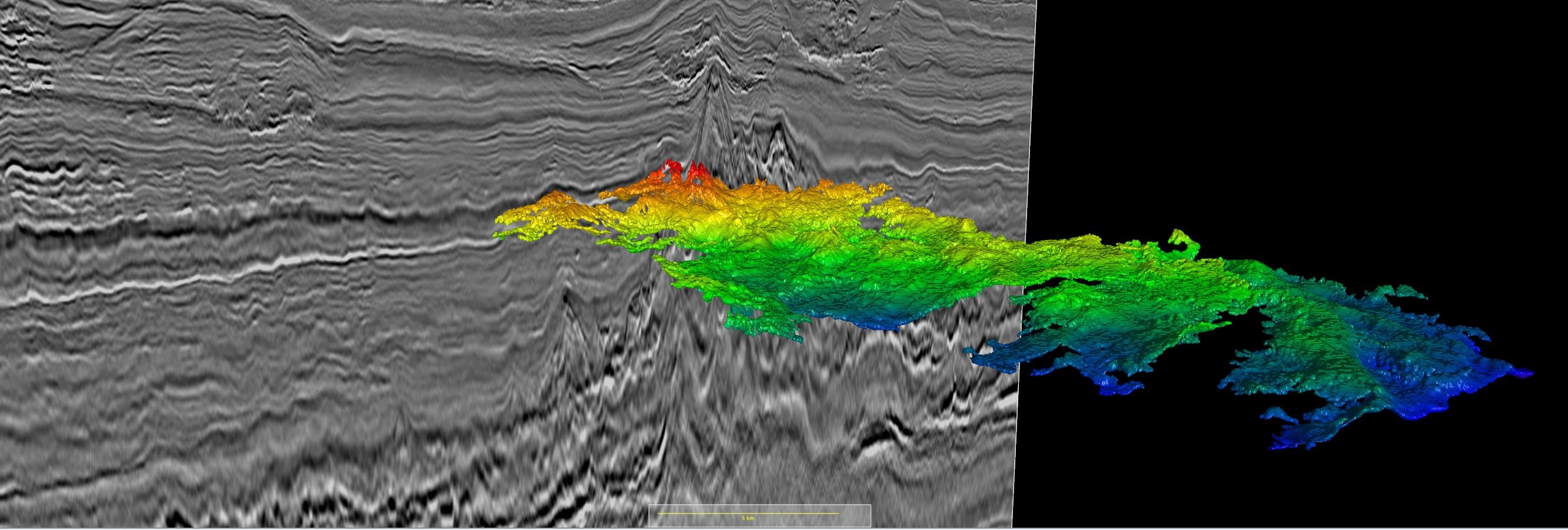
The Gabon North survey has revealed newly imaged sub-salt prospects in the post-rift sequences, undrilled syn-rift structures with large structural closures in the Gamba Sandstone target interval, and post-rift, interbedded marine shales and clastic sandstone reservoirs.
Hydrocarbon Potential
Two major petroleum systems are present offshore Gabon, separated by mobile evaporites known as the Ezanga Formation and having discrete source rock/reservoir pairs. The pre-salt petroleum system lies in the syn-rift and early post-rift sequences that were deposited during the break up of the continent of Gondwana in the Early Cretaceous period. The post-salt petroleum system comprises the sediments deposited during the continental drift of the West African passive margin. Various source rocks, reservoirs, and trapping mechanisms have historically characterized each petroleum system.
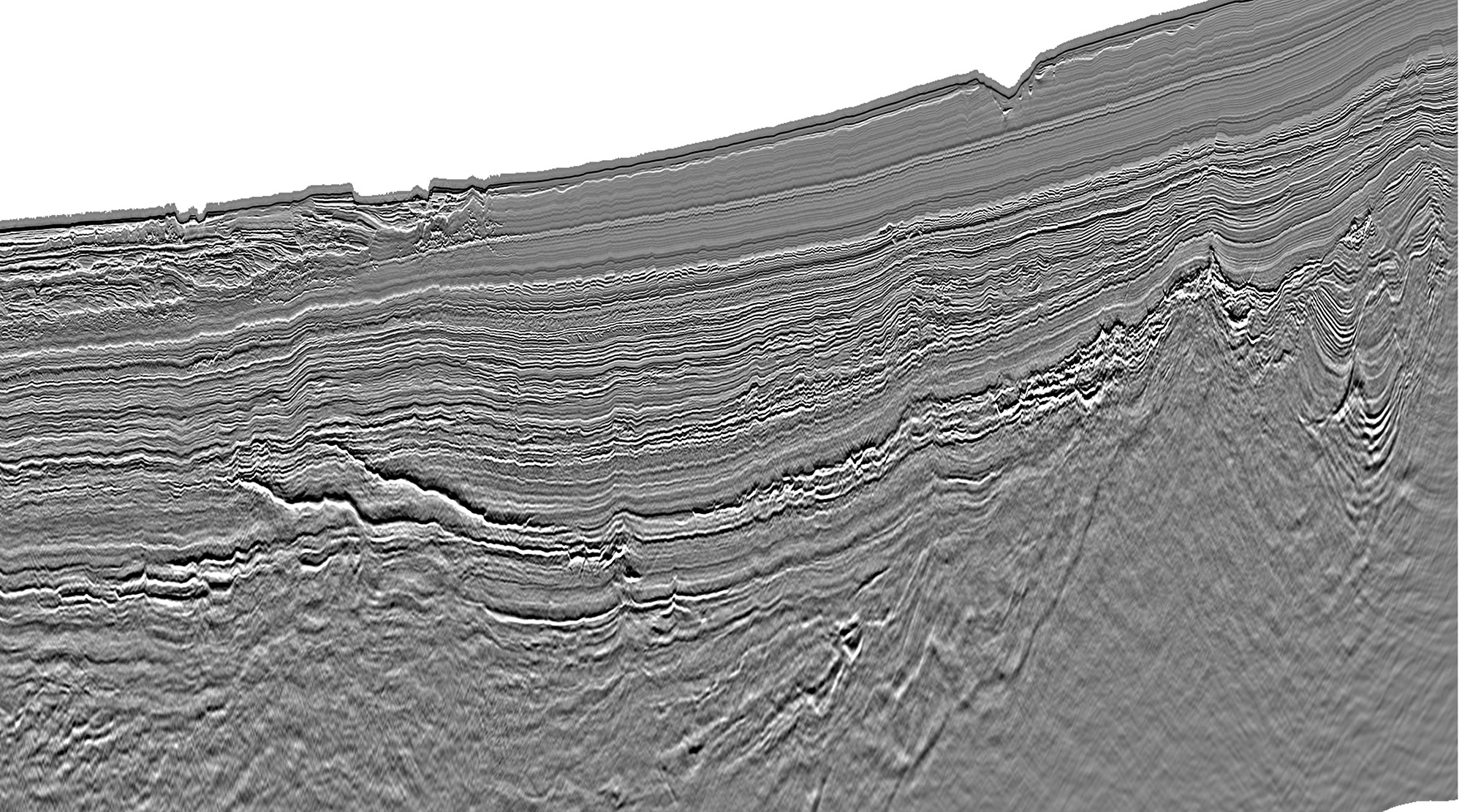
In South Gabon, the new 3D data reveals a startlingly clear image of the pre-salt syn-rift play systems, which previous generations of legacy seismic data have failed to resolve.
Sitting just below the salt, the transgressive Gamba Sandstone play relies on subtle low relief topology forming 4-way or fault-bounded structures. The difficulty of mapping such structures in the past is largely responsible for the previous dry wells. However, the Gamba Sands are no longer the only exploration objective as deeper intra-syn-rift targets are now revealed.
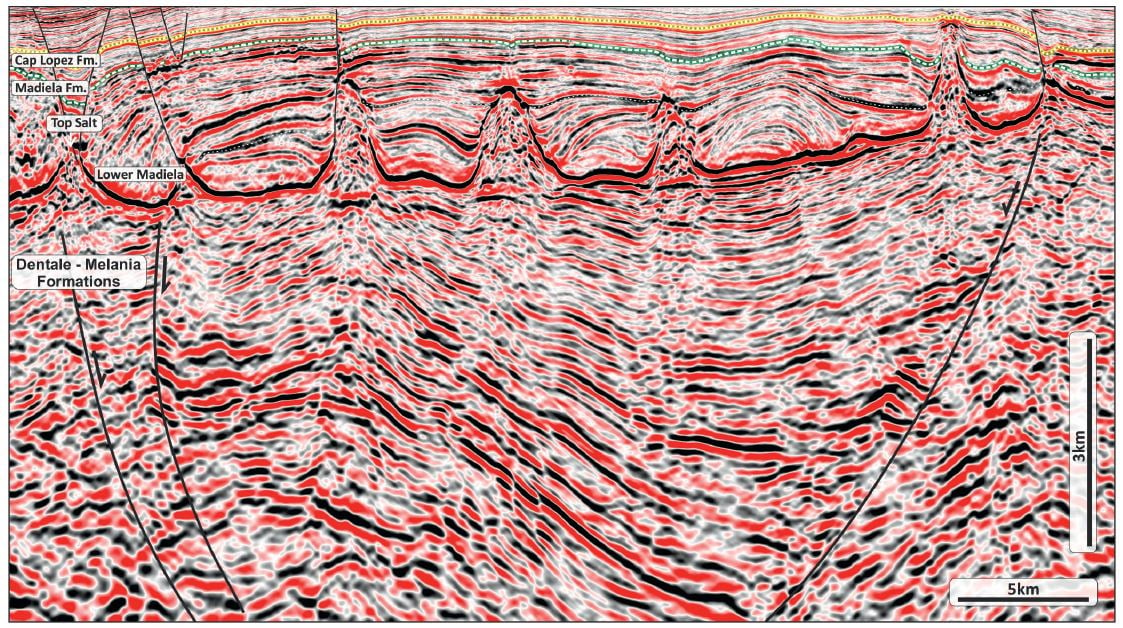
Structural mapping of the new 3D data shows a complex pattern of syn-rift structures, characterized by extensional faults on an en-echelon trend with strike direction between N-S and NW-SE. These listric roll-over anticlines (which may have a transpressional component) create large 4-way dip closures, each with areal closure of more than 150-200 km2 (see figure below). The syn-rift units of the Lower Cretaceous are imaged down to 10 km depth, showing fluvial and lacustrine sediments deposited within an active rift-graben. Multiple source rocks are present at various depths and with different maturity levels, generating mainly oil from the Dentale, Melania, and Kissenda formations.
Speak to a Specialist
Interested in a product demo or trial? Let us know your needs and we’ll connect you to the right person or team.
Book a Data Viewing
Want to see the latest seismic data solutions and imaging technologies in your region of interest or for the next license round? Book a data viewing with one of our experts.
Discuss Your Seismic Data Needs
Every need is different and we'd like the opportunity to discuss yours further. Speak to one of our data or geoscience experts to customize seismic solutions specific to your requirements.